The application of aromaticity and antiaromaticity to reaction mechanisms
Submitted by Jun Zhu on Sun, 04/30/2023 - 09:45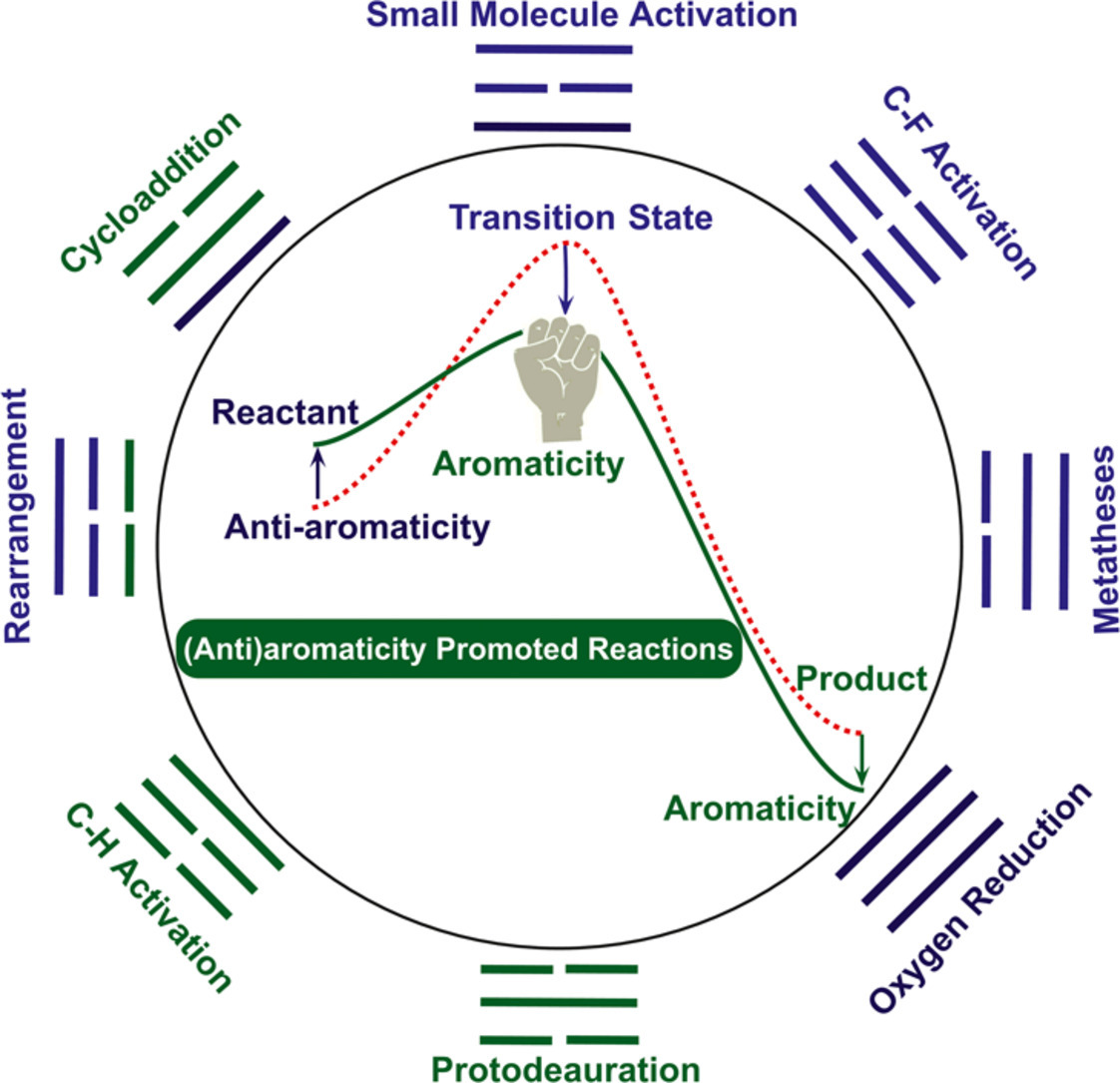
Aromaticity, in general, can promote a given reaction by stabilizing a transition state or a product via a mobility of π electrons in a cyclic structure. Similarly, such a promotion could be also achieved by destabilizing an antiaromatic reactant. However, both aromaticity and transition states cannot be directly measured in experiment. Thus, computational chemistry has been becoming a key tool to understand the aromaticity-driven reaction mechanisms.
