Antiaromaticity-Promoted Radical Stability in Boryl Heterocyclics and Its Application to Dinitrogen Activation: A Combined DFT and Machine Learning Study
Submitted by Jun Zhu on Thu, 08/07/2025 - 09:21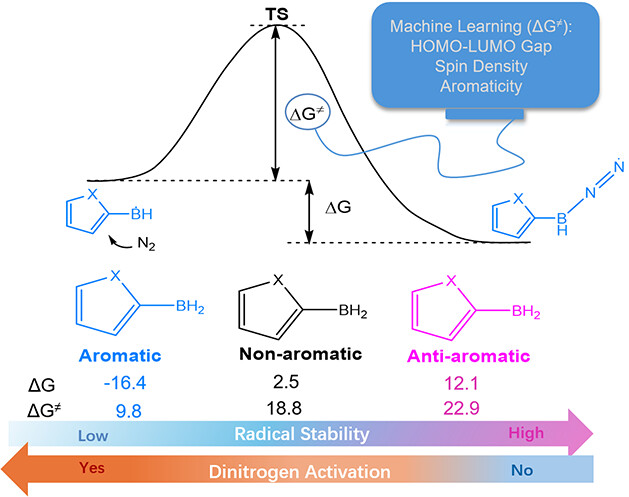
Aromaticity is one of the fundamental concepts in chemistry and generally brings additional thermodynamic stability to a compound. On the other hand, boron radicals have attracted increasing interest from both theoretical and experimental chemists due to their various applications. Here, we carry out density functional theory (DFT) calculations to explore the relationship between the (anti)aromaticity and stability of boron-centered radicals.