Reaction Mechanisms on Unusual 1,2‐Migrations of N‐Heterocyclic Carbene‐Ligated Transition Metal Complexes
Submitted by Jun Zhu on Thu, 09/05/2019 - 10:46
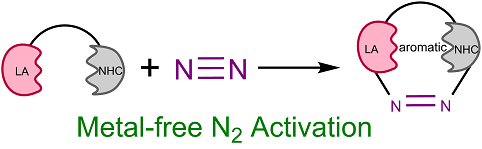
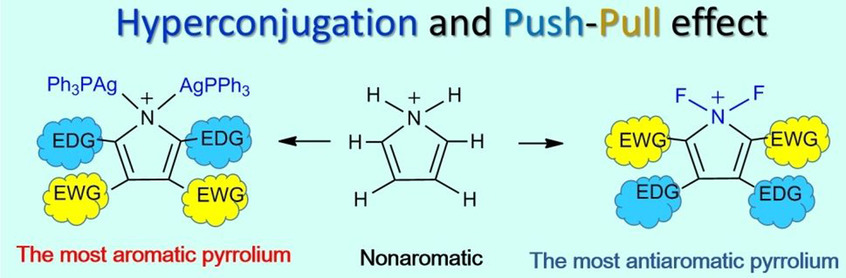
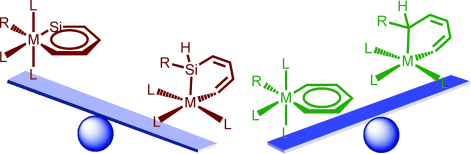
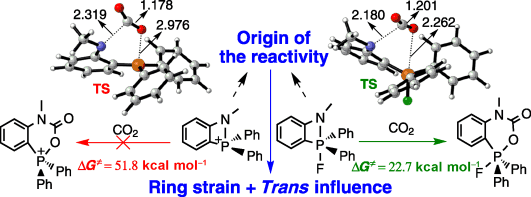
Unusual 1,2‐migration reactions of N‐heterocyclic carbene (NHC) on transition metals were investigated using density functional theory calculations. Our results reveal that the electronic properties, ring strain of the four‐membered ring, and aromaticity of NHC play crucial roles in the thermodynamics of such a 1,2‐migration.