Unexpected 1,2-Migration in Metallasilabenzenes: Theoretical Evidence for Reluctance of Silicon to Participate in π Bonding
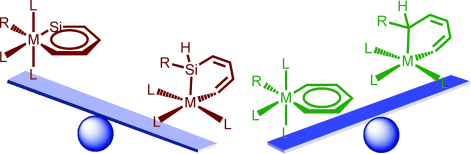
Density functional theory (DFT) calculations were carried out to investigate the 1,2-migration in metallasilabenzenes. The results suggested that the chloride migration of metallabenzenes is unfavorable due to the loss of aromaticity in the nonaromatic analogues. In sharp contrast, such a migration in metallasilabenzenes is favorable due to the reluctance of silicon to participate in π bonding. The migration of hydride and methyl group from the metal center to the silicon atom in metallasilabenzenes is computed to be also feasible. In addition, the π donor ligand and the third row transition metal can stabilize metallasilabenzenes. Thus, such a migration becomes less favorable thermodynamically and kinetically. These findings could be very helpful for synthetic chemists to realize the first metallasilabenzene.
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/asia.201402992/abstract
