Screening Borane Species for Dinitrogen Activation
Submitted by Jun Zhu on Wed, 08/05/2020 - 08:35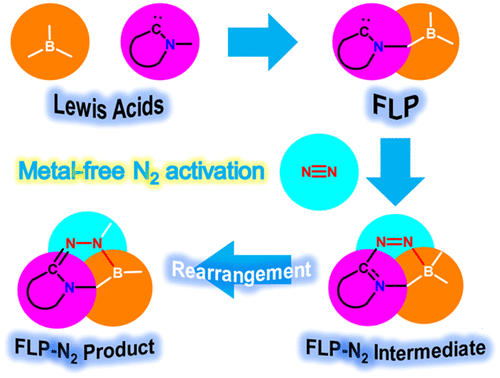
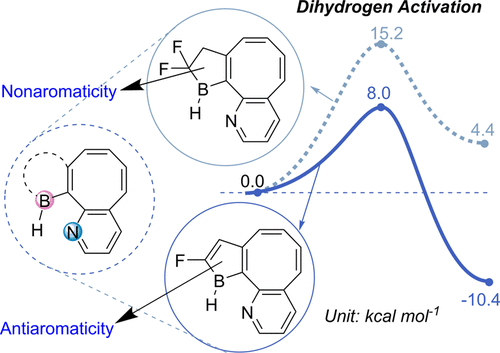
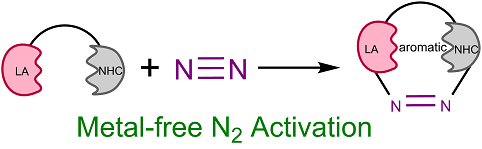
Activation of the strongest triplet bond in molecular nitrogen (N2) under mild conditions is particularly challenging. Recently, its fixation and reduction were achieved by highly reactive dicoordinated borylene species at ambient conditions, ripping the limits of harsh reaction conditions by metallic species. Less reactive species with a facile preparation could be desirable for next-generation N2 activation. Now density functional theory calculations reveal that tricoordinated boranes could be a potential candidate of N2 activation/functionalization.