Spin population determines whether antiaromaticity can increase or decrease radical stability
Submitted by Jun Zhu on Sat, 08/31/2024 - 08:48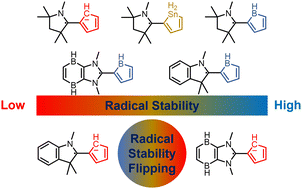
Aromaticity, as a classical and fundamental concept in chemistry, can enhance thermodynamic stability. In sharp contrast, a previous study showed that antiaromaticity rather than aromaticity can enhance the radical stability of α-methyl heterocyclic compounds. Here, we demonstrate a similar antiaromaticity-promoted radical stability when the methyl group is replaced by five-membered (alkyl)(amino)cyclics (AACs). More interestingly, when an AAC is fused with an antiaromatic ring, the radical stability could be either reduced or enhanced, depending on the spin population.
