Strategy for the Synthesis of Inverse Sandwich 1,4-Diarylbutadiene Dianionic Rare-Earth Metal Complexes via Directing Coupling of β-Aryl Vinyl Boron Reagents
Submitted by Jun Zhu on Sun, 02/22/2026 - 21:22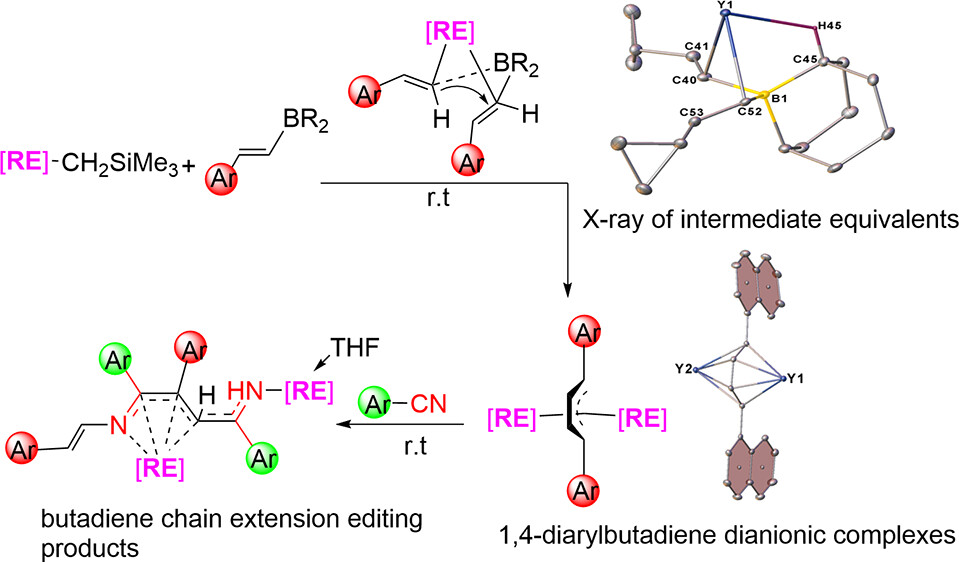
Aryl and vinyl boron reagents are widely employed in modern organic synthesis. However, the direct coupling of nucleophilic vinyl boron reagents to construct conjugated 1,4-diarylbutadiene dianionic (DABDA) motifs in the absence of additives remains a significant challenge. Here, we report for the first time the direct coupling of various β-aryl vinyl boron reagents, initiated by the rare-earth metal monoalkyl complexes for the synthesis of a number of rare-earth metal complexes featuring inverse sandwich DABDA motifs.