Antiaromaticity-Promoted Radical Stability in α-Methyl Heterocyclics
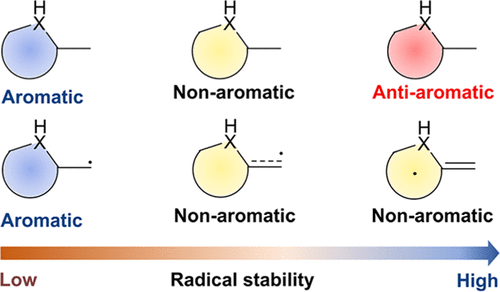
Aromaticity is a fundamental and important concept in chemistry, and usually, the enhancement of aromaticity brings additional thermodynamic stability to a compound. Moreover, since radicals can act as intermediates in chemical reactions, they have attracted considerable attention from both experimental and theoretical chemists for a long time. However, it remains unclear whether there is a relationship between the thermodynamic stability of cyclic planar radicals and their aromaticity. In this work, using various aromaticity indices including anisotropy of the induced current density analysis and nucleus-independent chemical shifts against the radical stabilization energy, we systematically investigated the relationship between aromaticity and the thermodynamic stability of α-methyl heterocyclics. Density functional theory calculations suggest that the stronger the antiaromaticity of the original form heterocyclics, the higher the thermodynamic stability of the corresponding radicals, which is in sharp contrast to the general knowledge that aromaticity brings compounds’ thermodynamic stabilities. The principal interacting spin orbital analysis shows that the stronger the π-bond formed between the heterocyclics and the α-methyl carbon, the more spin density the radicals tend to be distributed on the heterocyclics. Thus, the strong π-bonding is one of the factors for improving the thermodynamic stability of radicals.
