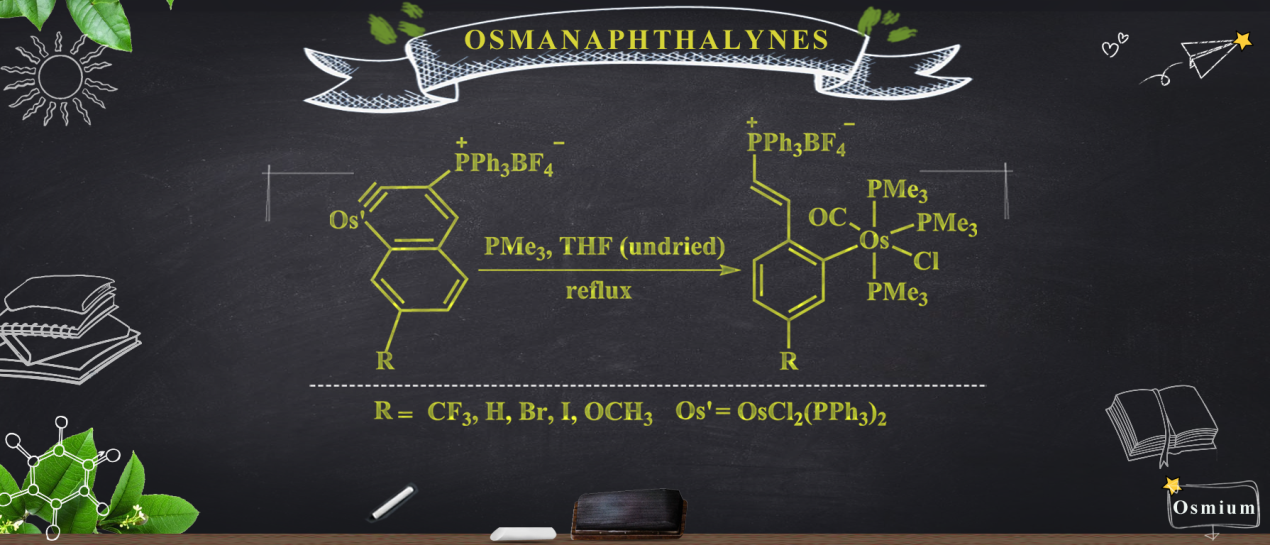
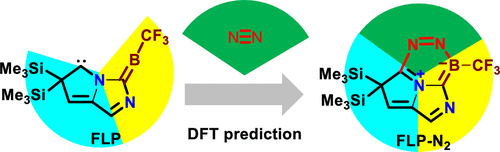
Theoretical Study on Reaction Mechanisms of Dinitrogen Activation and Coupling by Carbene-Stabilized Borylenes in Comparison with Intramolecular C-H Bond Activation
Submitted by Jun Zhu on Wed, 04/27/2022 - 09:21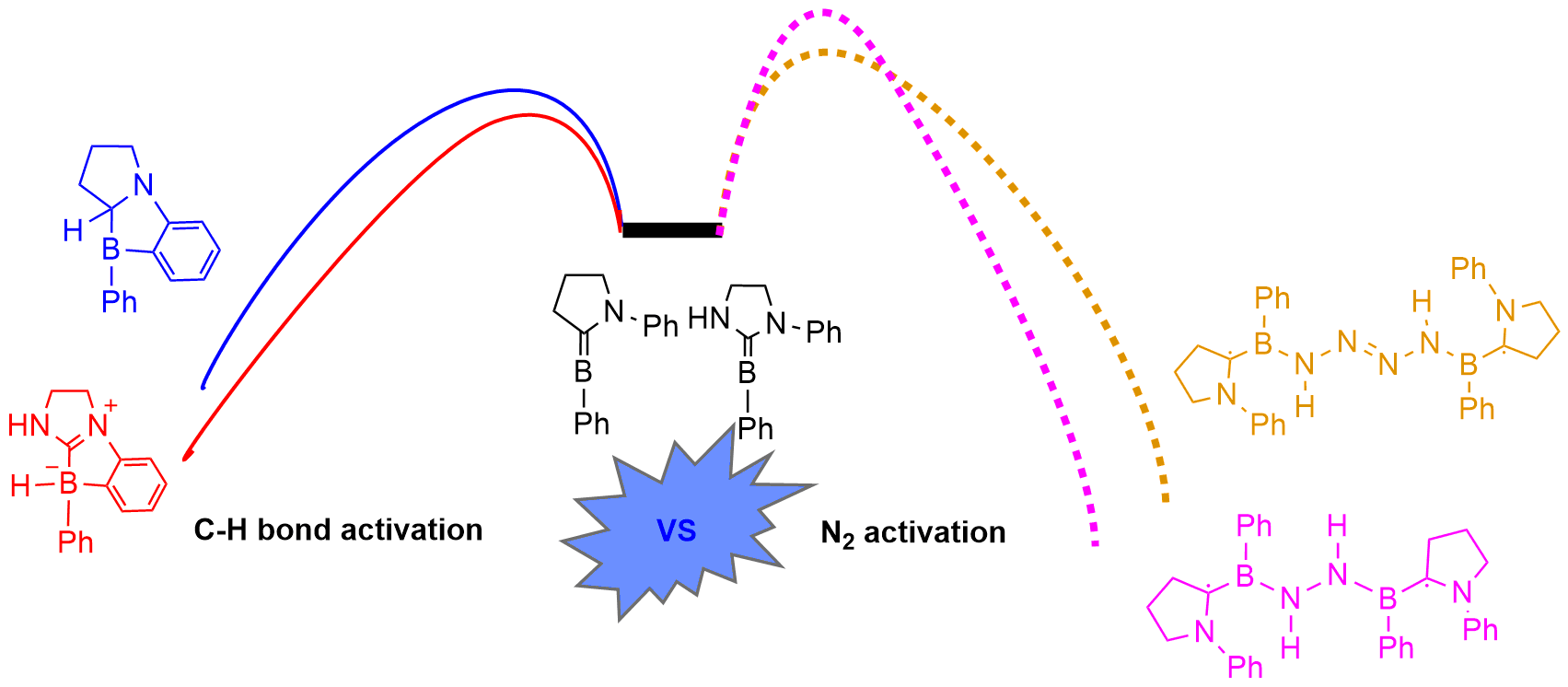
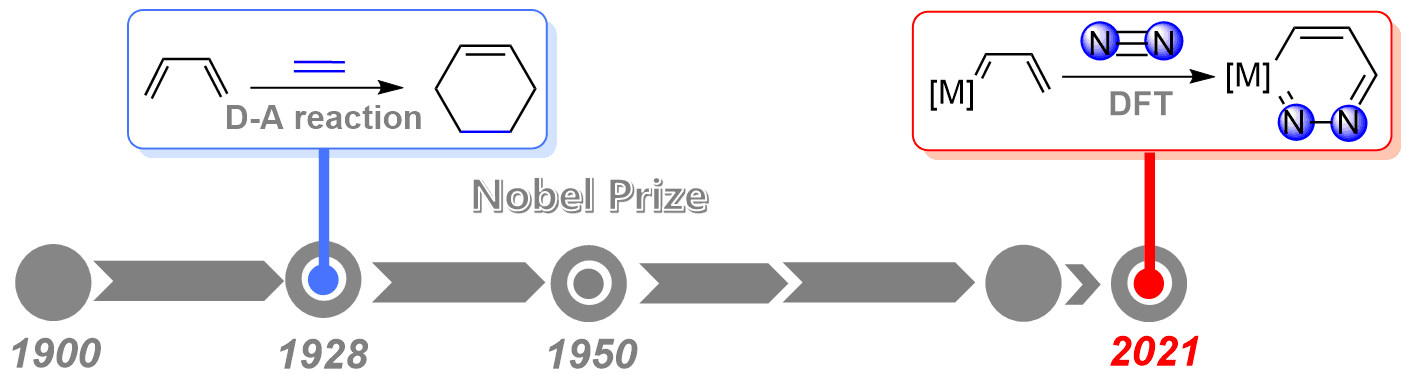
Dinitrogen (N2) activation is particularly challenging due to the significantly strong N≡N bond, let alone the catenation of two N2 molecules. Recent experimental study shows that cyclic (alkyl)(amino)carbene (CAAC)-stabilized borylenes are able to tackle N2 activation and coupling below room temperature. Here we carry out density functional theory calculations to explore the corresponding reaction mechanisms. The results indicate that the reaction barrier for the dinitrogen activation by the first borylene is slightly higher than that by the second borylene.