Nature Chemistry
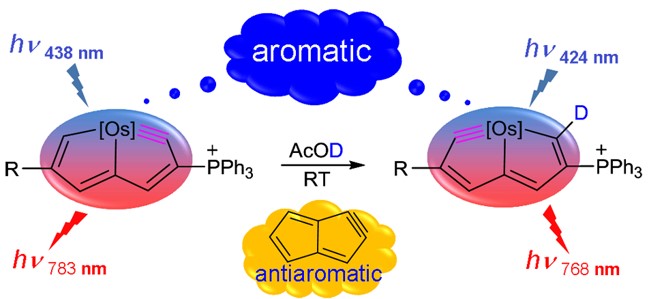


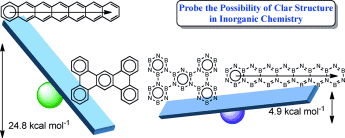
The Clar structure of polybenzenoid hydrocarbons (PBHs) have attracted considerable interest of both theoretical and experimental chemists since it was proposed in the 1950s. However, it remains unclear whether the Clar structure could exist in inorganic PBHs, the boron nitride (BN) analogues where the alternate boron and nitrogen atoms are used to replace the carbon atoms of PBHs. Here, we carry out thorough density functional theory (DFT) calculations to probe the possibility of Clar structures in BN analogues of PBHs.
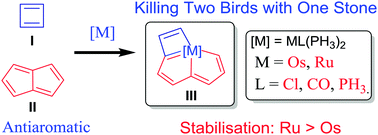
Density functional theory (DFT) calculations were carried out to investigate the stability and aromaticity of metallapentalocyclobutadienes. The results reveal unexpected higher stabilisation achieved with a 3d ruthenium fragment compared to the 4d osmium counterpart. Moreover, direct 1–3 metal–carbon bonding in the metallabutadiene unit of these two complexes is negligible.
http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2015/cc/c5cc08291a#!divAbstract
For details, please check the link at http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/asia.201500897/abstract
Communication
Unexpected Higher Stabilisation of Two Classical Antiaromatic Frameworks with a Ruthenium Fragment over Osmium Counterpart: Origin Probed by DFT Calculations
Jingjing Wu, Yulei Hao, Ke An and Jun Zhu
For details, please check the link at http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cphc.201500811/abstract.
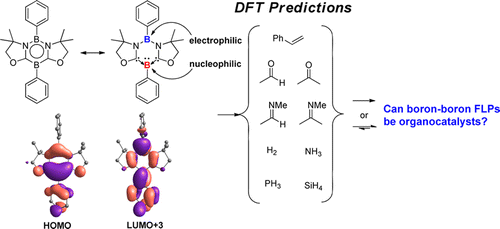
Recent progress in frustrated Lewis pairs (FLPs) has attracted increasing attention. However, most of the FLPs are composed of Lewis basic phosphines and Lewis acidic boranes. In 2015, Kinjo and co-workers reported the first intramolecular boron–boron FLP, namely, 1,3,2,5-diazadiborinine (1), which showed high regioselectivity in the reactions with methyl trifluoromethansulfonate, phenylacetylene, and CO2. More interestingly, the activation of CO2 was found to be reversible when the temperature was elevated to 90 °C.
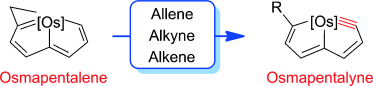
The synthesis of small cyclic metal carbynes is challenging due to the large angle strain associated with the highly distorted nonlinear triple bonds. Herein, we report a general route for the synthesis of five-membered cyclic metal carbyne complexes, osmapentalynes, by the reactions of an osmapentalene derivative with allene, alkyne, and alkene. Experimental observations and theoretical calculations document the aromaticity in the fused five-membered rings of osmapentalynes.
For details, please check the link at http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.201502412/abstract.

For details, please check the link at http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.201503578/abstract
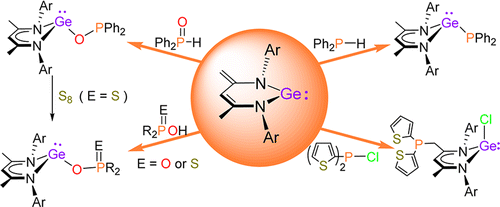
A series of phosphorus-substituted germanium(II) complexes, L1GeR [L1 = CH{(CMe)(2,6-iPr2C6H3N)}2; 2, R = PPh2; 4, R = OPPh2; 5a, R = OP(O)Ph2; 5b, R = OP(O) (OnBu)2; 6a, R = OP(S)Ph2; 6b, R = OP(S)(OEt)2], were synthesized through the direct activation of various organic phosphorus compounds by N-heterocyclic ylide-like germylene 1.
Copyright © 2026,
Theme Originally Created by Devsaran
